ONLINE SCHEDULING AND VIRTUAL CONSULTS AVAILABLE

Gum Disease and Dental Implants: Assessing Risks and Treatment Options
Are you considering dental implants but concerned about the potential risks associated with gum disease? Understanding the relationship between these two factors is crucial for making informed decisions about your oral health. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums. Left untreated, gum disease can lead to bone loss and tooth loss, creating challenges for dental implant placement.
That’s where the expertise of a skilled dentist in Plantation becomes invaluable. By assessing your gum health and providing tailored treatment options, we can help mitigate the risks associated with gum disease and ensure the success of your dental implant procedure. In this blog, we’ll explore the various aspects of gum disease and dental implants, offering guidance on how to navigate these concerns effectively. Whether you’re in need of preventive care or considering dental implants, our team is committed to supporting your journey to optimal oral health.
Understanding the Relationship Between Gum Disease and Dental Implants
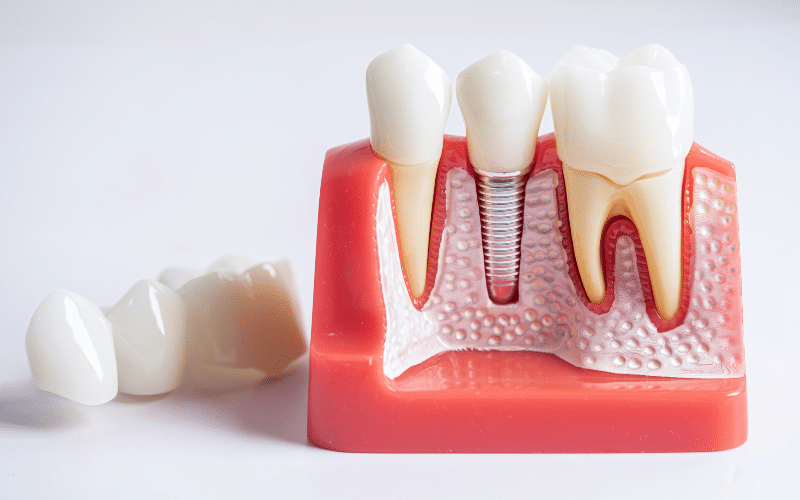
Gum disease, a prevalent oral health condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums, can significantly impact the success of dental implants. When gum disease is present, it can compromise the integrity of the supporting bone structure and soft tissues in the mouth, posing challenges for implant placement and osseointegration—the process by which the implant fuses with the jawbone. This compromised foundation can lead to various complications during and after the implant procedure, affecting the long-term stability and functionality of the implants.
Risks associated with placing implants in patients with gum disease
Placing dental implants in patients with existing gum disease presents inherent risks that dentists in Plantation must carefully assess. Patients with untreated or poorly managed gum disease may experience delayed healing, increased risk of implant failure, and potential complications such as peri-implantitis—a condition characterized by inflammation and infection around the implant site. Additionally, the presence of gum disease can exacerbate bone loss, further compromising the stability and longevity of dental implants.
Therefore, it’s crucial for a dentist in Plantation to thoroughly evaluate the periodontal health of patients before recommending dental implant treatment. By addressing any underlying gum disease issues proactively, dentists can optimize the chances of successful implant placement and ensure the long-term success of the restorative treatment.
Assessing Risks for Dental Implants in Patients with Gum Disease
Patients with gum disease face heightened risks of implant failure due to various factors:
- Increased inflammation and infection in the gums and surrounding tissues can impair the healing process after implant surgery.
- Gum disease can lead to bone loss in the jaw, compromising the stability and support of dental implants.
- Chronic periodontal infection may contribute to peri-implantitis, a condition that can cause bone loss around the implant.
- Poor oral hygiene habits and inadequate plaque control can exacerbate gum disease and implant-related complications.
- Smoking and certain systemic conditions can further escalate the risks of implant failure in patients with gum disease.
A thorough assessment by a dentist in Plantation is essential before proceeding with implant placement:
- Dentists possess the expertise to evaluate the extent and severity of gum disease in patients.
- Comprehensive periodontal assessments, including probing depths and X-rays, help identify underlying issues that may affect implant success.
- Dentists can develop personalized treatment plans to address gum disease and optimize oral health before implant surgery.
- Collaboration with periodontists or specialists may be necessary for complex cases requiring advanced periodontal care.
- Patient education and ongoing periodontal maintenance are crucial to minimize risks and ensure the long-term success of dental implants.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease Before Dental Implant Placement
Before proceeding with dental implant placement, patients with gum disease may undergo various treatment options to manage their condition:
- Non-surgical treatments: Dentists may recommend professional cleanings, scaling and root planing procedures, and antimicrobial therapy to control gum disease.
- Surgical interventions: In advanced cases, surgical treatments such as flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration may be necessary to address deep pockets and bone loss associated with gum disease.
Dental Implant Placement in Patients with a History of Gum Disease
A dentist in Plantation takes specific precautions when placing implants in patients with a history of gum disease to ensure optimal outcomes:
- Precautionary measures: Dentists thoroughly assess the patient’s oral health and periodontal status before implant surgery, ensuring that gum disease is adequately controlled.
- Long-term success rates: Despite the challenges, dental implants can have favorable long-term success rates in patients with a history of gum disease, especially with comprehensive treatment and diligent maintenance protocols.
Importance of Ongoing Periodontal Care After Dental Implant Placement
After dental implant placement, ongoing periodontal care is crucial to ensure the success and longevity of the implants:
Regular dental check-ups: Patients should schedule routine visits with their dentist in Plantation for professional examinations and cleanings to monitor gum health and detect any signs of inflammation or infection around the implants.
Customized maintenance plans: Dentists may provide personalized oral hygiene instructions and recommend specialized tools or products to help patients effectively clean around their implants and prevent gum disease.
Early intervention: Prompt treatment of any emerging issues, such as peri-implantitis or implant-related complications, can help preserve the integrity of the implants and surrounding tissues.
Lifestyle modifications: Patients are advised to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, tobacco cessation, and stress management, to support overall oral health and implant success.
Collaboration with dental professionals: Close communication between patients, dentists, and periodontists ensures comprehensive care and timely interventions to address any concerns related to gum health and dental implants.
Understanding the intricate relationship between gum disease and dental implants is paramount for successful implant treatment. With thorough assessment and proactive management by a skilled dentist in Plantation, patients can mitigate risks, undergo treatment with confidence, and enjoy the long-term benefits of restored oral health and function.